
Ravi Theja • 2024-01-31
LlamaIndex:在 RAG 混合搜索中通过 Alpha 调优提升检索性能
引言
检索适当的块(chunk)、节点或上下文是构建高效检索增强生成(RAG)应用的关键方面。然而,基于向量或嵌入的搜索可能对所有类型的用户查询都不有效。
为了解决这个问题,混合搜索结合了基于关键词的方法 (BM25) 和向量(嵌入)搜索技术。混合搜索有一个特定参数 Alpha,用于平衡关键词 (BM25) 搜索和向量搜索在为 RAG 应用检索正确上下文时的权重。(alpha=0.0 - 关键词搜索 (BM25),alpha=1.0 - 向量搜索)
但有趣之处在于:微调 Alpha 不仅仅是一项任务;它是一门艺术。实现理想的平衡对于释放混合搜索的全部潜力至关重要。这需要在 RAG 系统中针对不同类型的用户查询调整不同的 Alpha 值。
在这篇博文中,我们将探讨如何在 Weaviate 向量数据库中,使用 LlamaIndex 的 检索评估 模块,借助命中率 (Hit Rate) 和 MRR (Mean Reciprocal Rank) 指标,在有无重排器 (reranker) 的情况下调优 Alpha。
在深入实施之前,我们首先了解本文中将使用的不同查询类型和指标。
不同用户查询类型
RAG 应用中的用户查询因个人意图而异。对于这些不同的查询类型,微调 Alpha 参数至关重要。这个过程涉及将每个用户查询路由到特定的 Alpha 值,以实现有效的检索和响应合成。微软已经确定了各种用户查询类别,我们选择了一些用于调优我们的混合搜索。以下是我们考虑的不同用户查询类型:
- 网页搜索查询: 类似于通常输入到搜索引擎中的简短查询。
- 概念探寻查询: 需要详细的多句子回答的抽象问题。
- 事实探寻查询: 只有一个明确答案的查询。
- 关键词查询: 仅由关键标识词组成的简明查询。
- 包含拼写错误的查询: 包含打字错误、词序颠倒和常见拼写错误的查询。
- 精确子字符串搜索: 与原始上下文中的子字符串完全匹配的查询。
让我们看看每种不同用户查询类型的示例:
- 网页搜索查询
LLaMA 语言模型向非英语语言的迁移能力
2. 概念探寻查询
在最近的密集检索器研究中使用的双编码器架构是什么?
3. 事实探寻查询
在 FACTOID WIKI 中,英文维基百科数据转储被分割成多少个命题?
4. 关键词查询
GTR 检索器的召回率
5. 包含拼写错误的查询
与句子或段落检索相比,命题检索的优势是什么?
6. 精确子字符串搜索
GTR 检索器的前 k 个词。更细粒度
检索评估指标
我们将利用命中率 (Hit Rate) 和 MRR 指标进行检索评估。让我们来了解这些指标。
命中率 (Hit Rate)
命中率衡量正确块/上下文出现在前 k 个结果块/上下文中的查询比例。简单来说,它评估了我们的系统在其前 k 个块中正确识别该块的频率。
平均倒数排名 (MRR)
MRR 通过考虑每个查询的最高排名相关块/上下文的位置来评估系统的准确性。它计算所有查询中这些位置的倒数平均值。例如,如果第一个相关块/上下文在列表顶部,其倒数排名为 1。如果是第二个项目,倒数排名变为 1/2,以此类推。
本博文的其余部分分为两个主要部分:
- 在混合搜索中针对各种查询类型实现
Alpha调优。 - 分析两种不同文档数据集的结果
- 索引单个文档:《LLM 编译器》论文。
- 索引三个文档:《LLM 编译器》、《超越英语的 Llama》和 《Dense X Retrieval》论文。
您也可以从此处开始,继续参考此 Google Colab Notebook。
实现
我们将采用系统方法来实施实验工作流程,包括以下步骤:
- 数据下载。
- 数据加载。
- Weaviate 客户端设置。
- 索引创建和节点插入。
- 定义 LLM (GPT-4)
- 定义 CohereAI 重排器。
- 为各种查询类型生成合成查询。
- 定义 CustomRetriever。
- 检索评估和指标计算函数。
- 对不同查询类型和 Alpha 值进行检索评估。
让我们首先定义一些实现所需的基本函数。
get_weaviate_client- 设置 Weaviate 客户端。load_documents- 从文件路径加载文档。create_nodes- 使用文本分割器对文档进行分块创建节点。connect_index- 连接到 Weaviate 索引。insert_nodes_index- 将节点插入索引。
def get_weaviate_client(api_key, url):
auth_config = weaviate.AuthApiKey(api_key=api_key)
client = weaviate.Client(
url=url,
auth_client_secret=auth_config
)
return client
def load_documents(file_path, num_pages=None):
if num_pages:
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(input_files=[file_path]).load_data()[:num_pages]
else:
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(input_files=[file_path]).load_data()
return documents
def create_nodes(documents, chunk_size=512, chunk_overlap=0):
node_parser = SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=chunk_size, chunk_overlap=chunk_overlap)
nodes = node_parser.get_nodes_from_documents(documents)
return nodes
def connect_index(weaviate_client):
vector_store = WeaviateVectorStore(weaviate_client=weaviate_client)
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(vector_store=vector_store)
index = VectorStoreIndex([], storage_context=storage_context)
return index
def insert_nodes_index(index, nodes):
index.insert_nodes(nodes)- 下载数据
!wget --user-agent "Mozilla" "https://arxiv.org/pdf/2312.04511.pdf" -O "llm_compiler.pdf"
!wget --user-agent "Mozilla" "https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.01055.pdf" -O "llama_beyond_english.pdf"
!wget --user-agent "Mozilla" "https://arxiv.org/pdf/2312.06648.pdf" -O "dense_x_retrieval.pdf"2. 加载数据
# load documents, we will skip references and appendices from the papers.
documents1 = load_documents("llm_compiler.pdf", 12)
documents2 = load_documents("dense_x_retrieval.pdf", 9)
documents3 = load_documents("llama_beyond_english.pdf", 7)
# create nodes
nodes1 = create_nodes(documents1)
nodes2 = create_nodes(documents2)
nodes3 = create_nodes(documents3)3. 设置 Weaviate 客户端
url = 'cluster URL'
api_key = 'your api key'
client = get_weaviate_client(api_key, url)4. 创建索引并插入节点。
index = connect_index(client)
insert_nodes_index(index, nodes1)5. 定义 LLM
# Deing LLM for query generation
llm = OpenAI(model='gpt-4', temperature=0.1)6. 创建合成查询
我们将按之前讨论的方式创建查询,您可以在 Notebook 中查看每种查询类型的提示和代码。下方显示代码片段以供参考。
queries = generate_question_context_pairs(
nodes,
llm=llm,
num_questions_per_chunk=2,
qa_generate_prompt_tmpl = qa_template
)7. 定义重排器
reranker = CohereRerank(api_key=os.environ['COHERE_API_KEY'], top_n=4)8. 定义 CustomRetriever
我们将定义 CustomRetriever 类,以在有无重排器的情况下执行检索操作。
class CustomRetriever(BaseRetriever):
"""Custom retriever that performs hybrid search with and without reranker"""
def __init__(
self,
vector_retriever: VectorIndexRetriever,
reranker: CohereRerank
) -> None:
"""Init params."""
self._vector_retriever = vector_retriever
self._reranker = reranker
def _retrieve(self, query_bundle: QueryBundle) -> List[NodeWithScore]:
"""Retrieve nodes given query."""
retrieved_nodes = self._vector_retriever.retrieve(query_bundle)
if self._reranker != None:
retrieved_nodes = self._reranker.postprocess_nodes(retrieved_nodes, query_bundle)
else:
retrieved_nodes = retrieved_nodes[:4]
return retrieved_nodes
async def _aretrieve(self, query_bundle: QueryBundle) -> List[NodeWithScore]:
"""Asynchronously retrieve nodes given query.
Implemented by the user.
"""
return self._retrieve(query_bundle)
async def aretrieve(self, str_or_query_bundle: QueryType) -> List[NodeWithScore]:
if isinstance(str_or_query_bundle, str):
str_or_query_bundle = QueryBundle(str_or_query_bundle)
return await self._aretrieve(str_or_query_bundle)9. 定义用于检索评估和指标计算的函数
我们将研究使用不同 alpha 值在有无重排器的情况下检索器的性能。
# Alpha values and datasets to test
alpha_values = [0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0]
# Function to evaluate retriever and return results
async def evaluate_retriever(alpha, dataset, reranker=None):
retriever = VectorIndexRetriever(index,
vector_store_query_mode="hybrid",
similarity_top_k=10,
alpha=alpha)
custom_retriever = CustomRetriever(retriever,
reranker)
retriever_evaluator = RetrieverEvaluator.from_metric_names(["mrr", "hit_rate"], retriever=custom_retriever)
eval_results = await retriever_evaluator.aevaluate_dataset(dataset)
return eval_results
# Function to calculate and store metrics
def calculate_metrics(eval_results):
metric_dicts = []
for eval_result in eval_results:
metric_dict = eval_result.metric_vals_dict
metric_dicts.append(metric_dict)
full_df = pd.DataFrame(metric_dicts)
hit_rate = full_df["hit_rate"].mean()
mrr = full_df["mrr"].mean()
return hit_rate, mrr10. 检索评估
在这里,我们对不同的查询类型(数据集)和 alpha 值进行检索评估,以了解哪种 alpha 值适用于哪种查询类型。您需要相应地接入重排器,以计算有无重排器时的检索评估。
# Asynchronous function to loop over datasets and alpha values and evaluate
async def main():
results_df = pd.DataFrame(columns=['Dataset', 'Alpha', 'Hit Rate', 'MRR'])
for dataset in datasets_single_document.keys():
for alpha in alpha_values:
eval_results = await evaluate_retriever(alpha, datasets_single_document[dataset])
hit_rate, mrr = calculate_metrics(eval_results)
new_row = pd.DataFrame({'Dataset': [dataset], 'Alpha': [alpha], 'Hit Rate': [hit_rate], 'MRR': [mrr]})
results_df = pd.concat([results_df, new_row], ignore_index=True)
# Determine the grid size for subplots
num_rows = len(datasets_single_document) // 2 + len(datasets_single_document) % 2
num_cols = 2
# Plotting the results in a grid
fig, axes = plt.subplots(num_rows, num_cols, figsize=(12, num_rows * 4), squeeze=False) # Ensure axes is always 2D
for i, dataset in enumerate(datasets_single_document):
ax = axes[i // num_cols, i % num_cols]
dataset_df = results_df[results_df['Dataset'] == dataset]
ax.plot(dataset_df['Alpha'], dataset_df['Hit Rate'], marker='o', label='Hit Rate')
ax.plot(dataset_df['Alpha'], dataset_df['MRR'], marker='o', linestyle='--', label='MRR')
ax.set_xlabel('Alpha')
ax.set_ylabel('Metric Value')
ax.set_title(f'{dataset}')
ax.legend()
ax.grid(True)
# If the number of datasets is odd, remove the last (empty) subplot
if len(datasets_single_document) % num_cols != 0:
fig.delaxes(axes[-1, -1]) # Remove the last subplot if not needed
# Adjust layout to prevent overlap
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Run the main function
asyncio.run(main())分析结果
完成实现阶段后,我们现在开始分析结果。我们进行了两组实验:一组针对单个文档,另一组针对多个文档。这些实验在 alpha 值、用户查询类型以及是否包含重排器方面有所不同。附图显示了结果,重点关注命中率 (Hit Rate) 和 MRR(平均倒数排名)作为检索评估指标。
P请记住,以下观察结果仅针对我们研究中使用的数据集。我们鼓励您使用自己的文档进行实验,并得出您的相关观察和结论。
使用单个文档
没有重排器
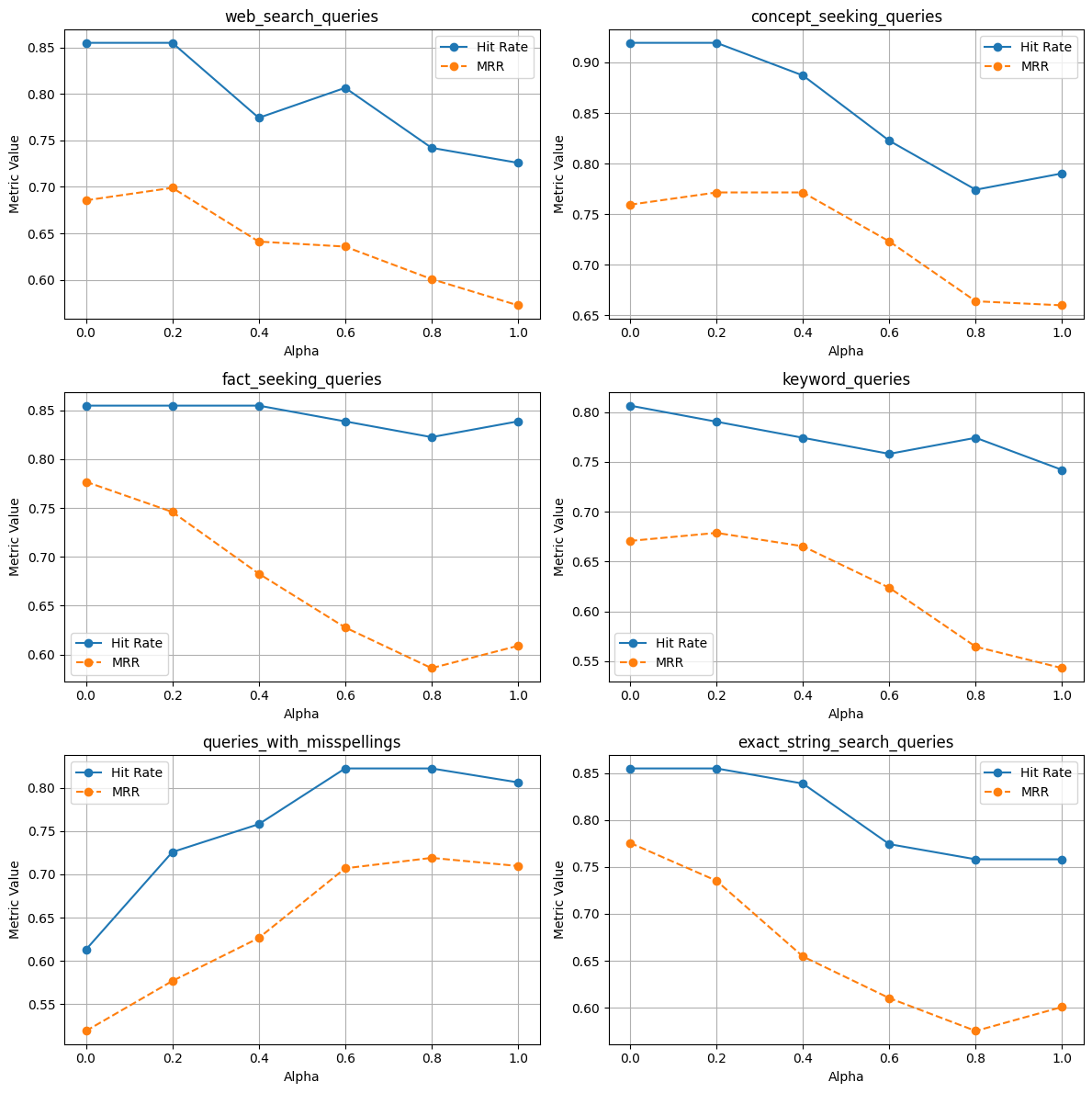
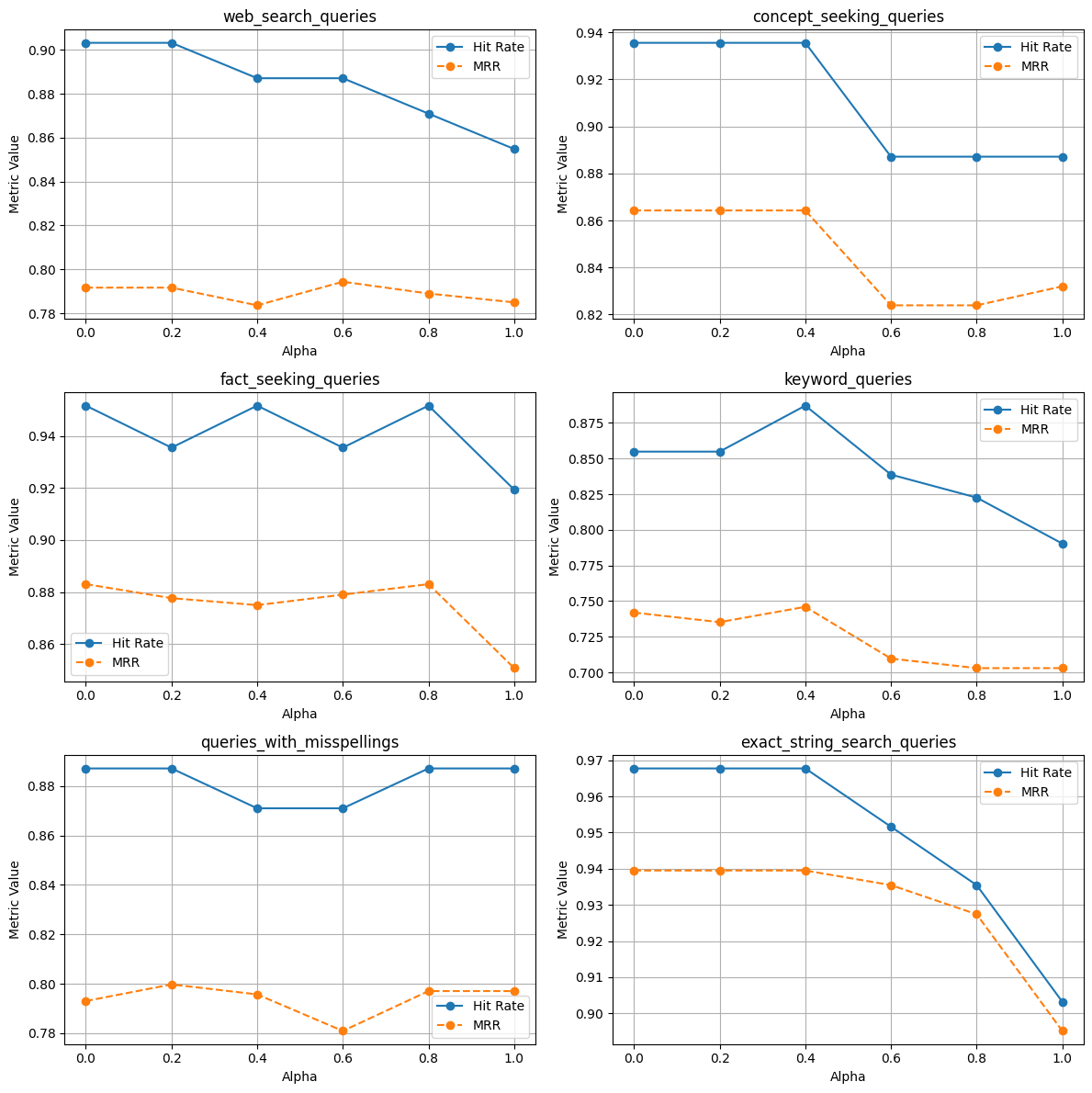
使用重排器
使用多个文档
没有重排器
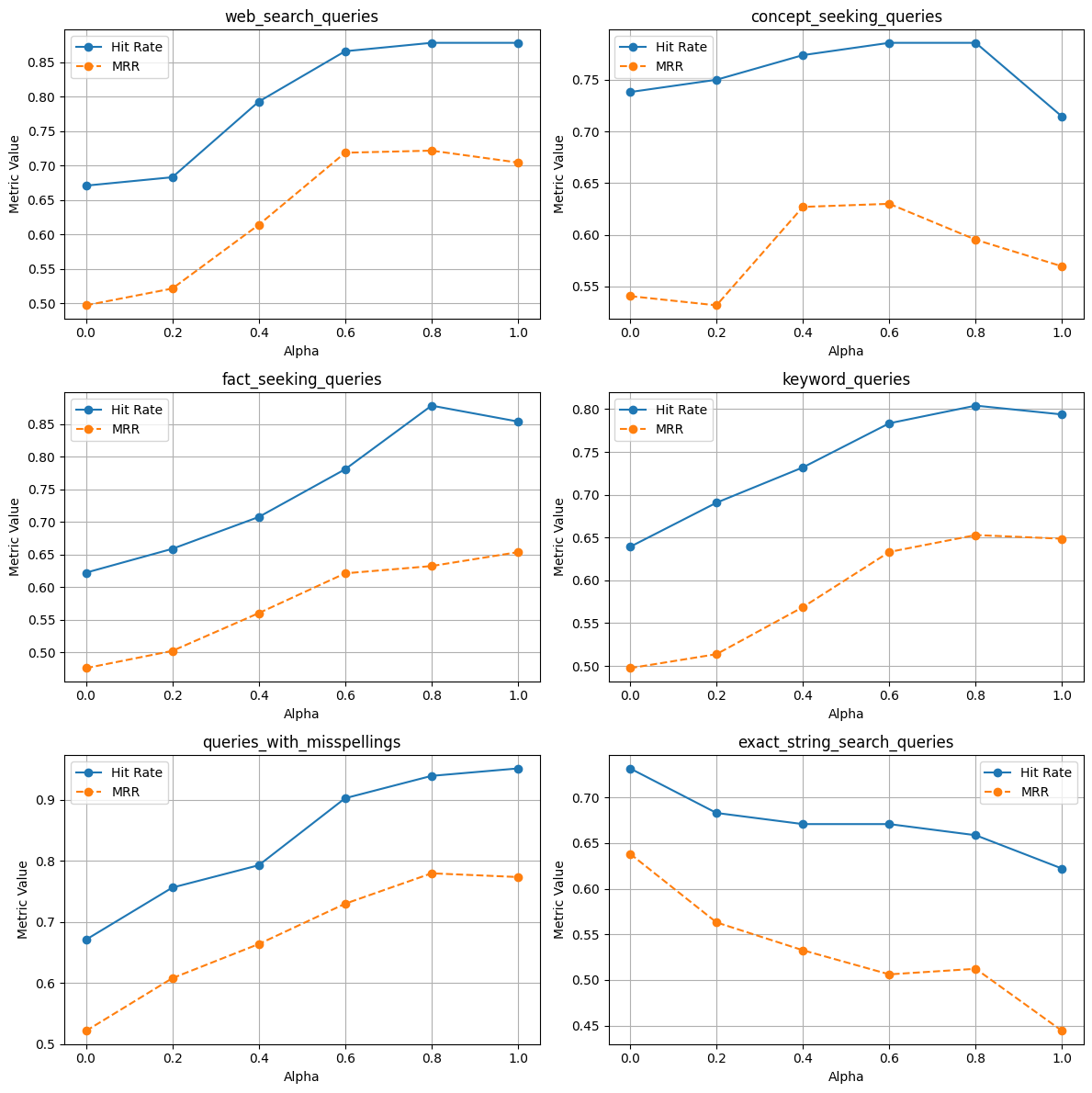
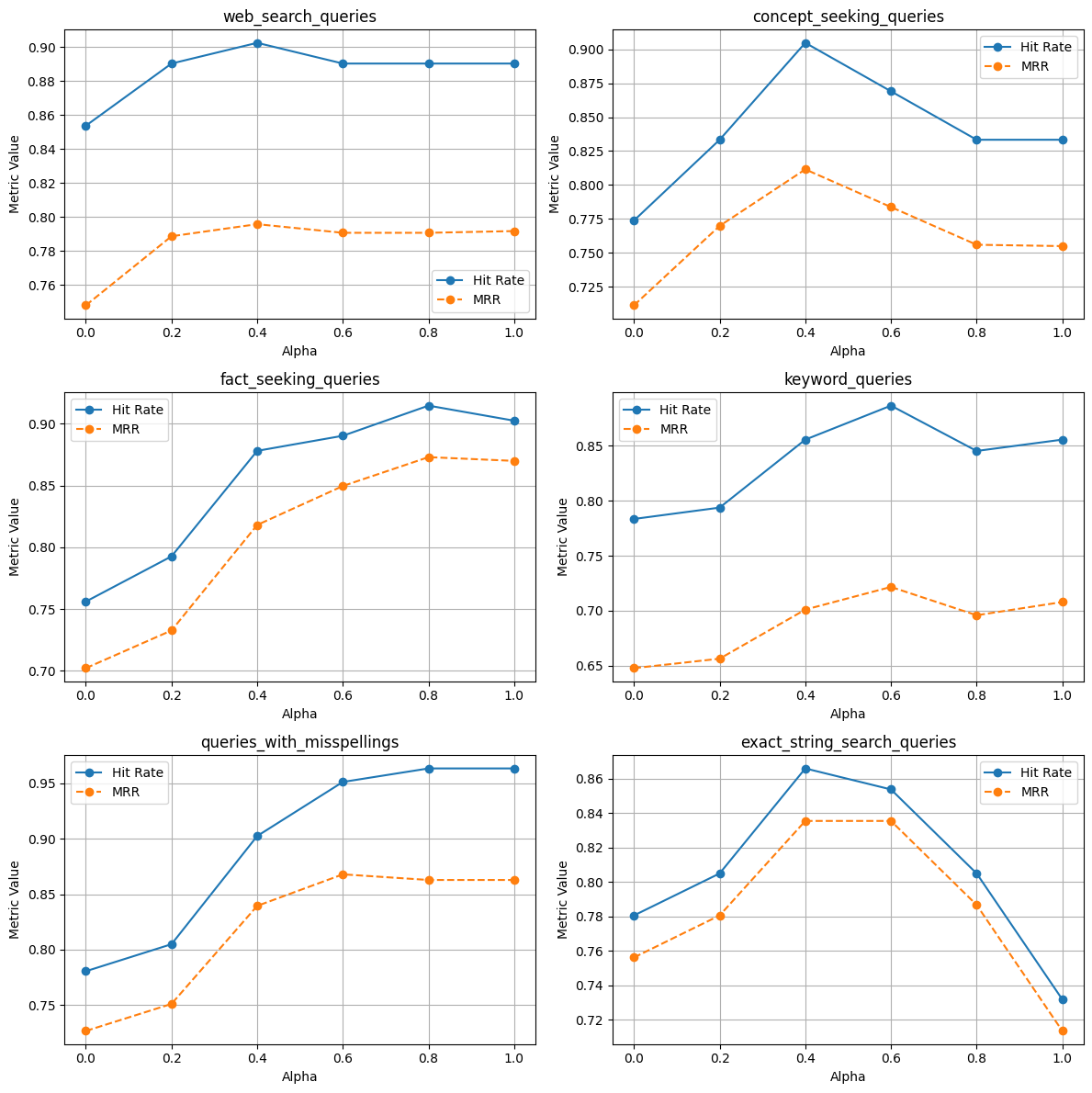
使用重排器
观察结果
- 在单个和多个文档索引中,借助重排器,命中率和 MRR 都有提升。这再次证明了在 RAG 应用中使用重排器非常有用。
- 尽管大多数时候混合搜索优于关键词/向量搜索,但在 RAG 应用中应根据用户查询类型仔细评估。
- 索引单个文档和多个文档时的行为不同,这表明随着您向索引添加文档,最好始终调优 alpha 值。
- 让我们更深入地分析不同的查询类型:
- 网页搜索查询
— 无论索引单个还是多个文档,也无论有无重排器,使用 alpha=0.2/0.6 的混合搜索 MRR 都更高。
— 无论是索引单个还是多个文档,也无论有无重排器,使用 alpha=1.0 的命中率都更高。
- 概念探寻查询
— 在多个文档索引中,混合搜索(使用不同的 alpha 值)的 MRR 和命中率更高。
— 在单个文档索引中,当 Alpha=0.0 时,MRR 和命中率更高,这表明关键词搜索效果更好。需要注意的是,有无重排器对 MRR 的影响不同。
- 事实探寻查询
— 在多个文档索引中,有无重排器的混合搜索的 MRR 和命中率更高。
— 在单个文档索引中,使用重排器的混合搜索的 MRR 和命中率更高,而没有重排器时关键词搜索(alpha=0.0)效果更好。
- 关键词查询
— 在多个文档索引中,有无重排器的混合搜索的 MRR 和命中率更高。
— 在单个文档索引中,使用重排器的混合搜索的 MRR 和命中率更高,而没有重排器时关键词搜索效果更好。(尽管 alpha=0.2 时 MRR 略高)
- 包含拼写错误的查询
— 在单个和多个文档索引中,有无重排器的混合搜索的 MRR 和命中率更高。(尽管在某些情况下,alpha=1.0 的混合搜索效果更好)。
— 这也表明向量搜索在处理包含拼写错误的查询时表现更好,因为关键词搜索在这种情况下会失效。
- 精确子字符串搜索
— 在单个文档索引中,有无重排器的关键词搜索的 MRR 和命中率更高;在多个文档索引中,没有重排器的关键词搜索的 MRR 和命中率更高。
— 在多个文档索引中,使用重排器的混合搜索(alpha=0.4)的 MRR 和命中率更高。
后续计划?
在这篇博文中,我们探讨了在混合搜索系统中针对一系列查询类型进行 Alpha 调优。有趣的是,索引单个文档或多个文档时结果会有所不同。接下来,您可以考虑使用来自不同领域的文档进行实验,并针对各种查询类型采用不同的查询长度。如果您有任何值得注意的观察,我们鼓励您在评论中与我们分享。与更广泛的社区讨论这些发现肯定会很有趣。



